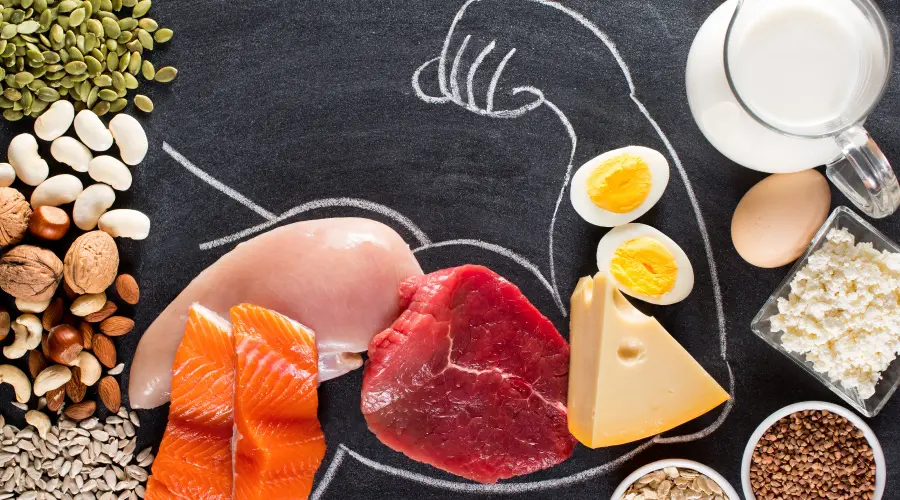
What’s a dream body – Herculean style or skinny look? Muscular, saggy, plump, robust, fatty, or toned-up? Well, it’s undoubtedly a matter of your choice; however, some things remain unchanged for years – a muscular body has always been a sign of health and strength. Not only do muscles look better than body fat, but they are also quite helpful for doing everyday activities. If you have thought about a plan for building muscle, let’s do it together. We will help you make a meal plan, count macros, which are essential for body building diet, and teach you everything about nutrition for muscle growth.
Page Contents
Improving Your Figure With A Muscle Building Diet
Muscle growth can also be called hypertrophy. It is the increase in the volume of muscle tissue due to the enlargement of its cells. It is mainly contributed by enlarged muscle glycogen storage. Athletes use a combination of strength training, diet, and the right balance of nutrients to give rise to muscle hypertrophy.
Muscle growth doesn’t solely mean pumping up your body to the limits for a bodybuilding competition. It’s about having a healthier, more muscular, leaner body for both women and men. An athletic body type and muscular look has always been perceived as a sign of strength and confidence.
The Pros And Cons Of Gaining Muscle Mass
Everything we do has its pros and cons. You may shift the balance to the opposing side when you put too much effort into something, even with the best intentions. The same happens with muscle gain. Let’s learn more.
Pros of Gaining Muscle Mass
1. Muscle mass increases metabolic rate
The muscle tissue uses energy stored by fat tissue. By gaining muscle through strength training, you increase your energy requirements which, in its turn, increases your metabolic rate. The higher the metabolic rate you have, the more calories you burn.
2. Muscle mass increases bones density
Building up your muscles strengthens your bones, tendons, and ligaments. It is driven by constant training; your bones get used to the extra tension they need to withstand and so become denser and stiffer. Athletes use muscle training not only to improve athletic performance but to reduce everyday injuries.
Building up your core strength improves your balance and coordination; that’s why it’s important to do strength training when aging as we become more susceptible to minor injuries.
3. Muscle mass makes everyday routine easier
How often do you ask someone to open a jar of jam or a bottle of water? Have you been struggling to carry the shopping bags back home or just move a box with “one-day-I-will-use-it” stuff?
While it may seem cute to help a person with such things, it may become quite annoying with time. Besides, waiting for everyone to help you is not the best option either.
That’s when you need to consider adding a strength training regimen to your daily routine. Step by step, exercise by exercise, you’ll make your muscles stronger and will make do without anybody’s help – a tiny fraction of your personal freedom.
4. Muscle mass gives you body shape
When you build muscles, your appearance improves as well. It’s certainly better than having saggy arms, weak legs, and a fatty belly. Besides, you’ll be able to buy the clothes you want, and you will never shy away from the beach walk.
5. Decreased disease risks
Having a muscular body is a positive “side-effect” of strength training. The main thing you reach is your general health improvement. Physically active people are less susceptible to diseases than those with a mainly sedentary lifestyle. By improving your cardiovascular function, you improve your blood chemistry and lower the risks of heart diseases and diabetes.
Cons of Gaining Muscle Mass
1. Temporary weight gain
Trying to lose weight and build muscle mass simultaneously, you may notice a gain in weight at the beginning. As long as your muscle mass increases noticeably initially, it may outpace your weight loss. To avoid that, keep track of your nutrition, and focus on more repetitions and lighter weights.
2. Stress Fractures
Embarking on a workout program too quickly, you may experience stress fractures of your bones – tiny cracks in your bone [1], which appear when you lift more weight than you can handle. It’s essential to increase the intensity of workouts gradually, while gaining enough strength for heavier weights.
3. Muscle pain and ache
Another potential downside is due to overstrain. Lifting too much weight could result in a muscle tear and damage to ligaments and tendons or the surrounding soft tissue.
4. Reverse anorexia
Surprised to see anorexia mentioned? While anorexia is a constant decrease of body weight, which can lead to detrimental and irreversible changes to your body and mind, reverse anorexia is about the obsession with a bigger body and the size of your muscles. A bodybuilder can be driven, at first, by healthy ideas, but with time, his perception of a body becomes inadequate (looks too small). It leads to an obsession with muscle building diet plans, overuse of supplements, limited social activities, etc.
When starting the muscle-building process, remember about moderation and balance, which are crucial to success.
Crucial Tips When Creating A Muscle-Building Plan
1. Eat breakfast
The start of the day must be filled with energy that will help you to perform your life/work functions efficiently. Besides having a substantial breakfast, you are less likely to eat lots of snacks throughout the day, giving preference to main meals. Your best options include omelets, cottage cheese, oatmeal with dried fruit, etc.
2. Eating split meals at the regular time
If you noticed that three meals per day leave you hungry in between, make some changes. Instead of eating breakfast, lunch, and dinner, gulping up everything you see, have some healthy snacks meanwhile. Keeping your food intake up, you’ll decrease the portions of main meals and have fewer cravings during the day. Moreover, your stomach size will get smaller, as you will stop eating everything at once.
Keep to your eating timing; it will help you digest food quicker.
3. Increase protein intake
To maintain and increase muscle mass, you need to eat at least 1g per 454g of body weight. The easiest way to get this amount is to add protein to each meal protein sources with each meal including:
• Red meat (beef, pork, lamb, etc.).
• Poultry (chicken, turkey, duck, etc.).
• Fish (tuna, salmon, sardines, mackerel, etc.).
• Eggs.
• Dairy (milk, cheese, cottage cheese, quark, yogurt, etc.).
Control your carbs intake
Carbohydrates replenish your energy stores; however, we typically eat more than we need. Substitute white carbs with whole grains. Instead of sweets and cookies, eat some fruits to get fiber and enough “natural” sugar.
4. Add fruits and vegetables
Most vegetables (not all) are low-calorie. They can quickly make you full without giving you tons of calories. They are also rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, which help digestion.
5. Control fats intake
Avoid trans-fat and margarine; they raise “bad” cholesterol and lower “good” cholesterol. A diet full of trans fats increases the risk of heart disease and obesity.
Healthy fats improve health as they digest slowly.
6. Water balance
Every intensive workout causes sweating and excessive water loss. Drinking water prevents dehydration, stimulates muscle recovery, and suppresses the feeling of hunger during training.
Calorie Needs and Macronutrients
Body building diet for bulking doesn’t mean eating more. It requires proper planning to provide your body with energy and maintain progress.
How Many Calories Do You Need?
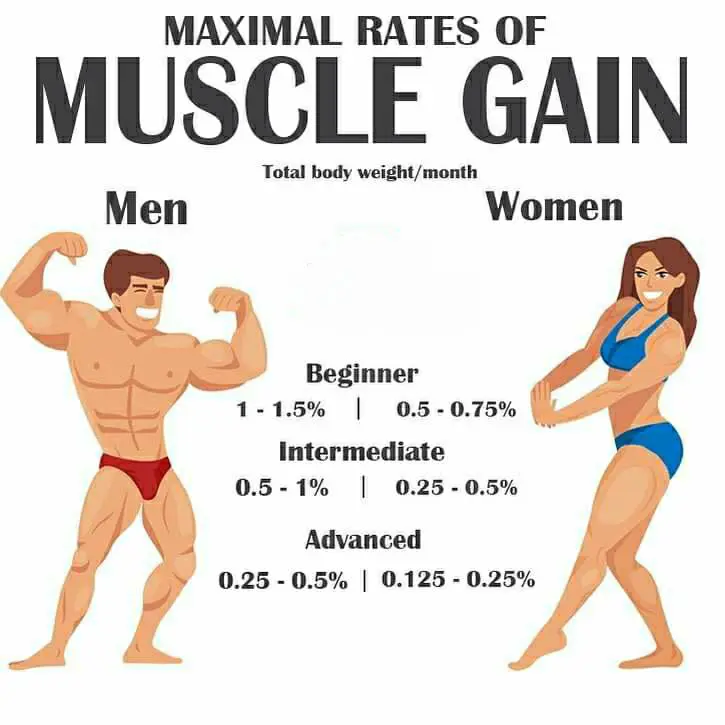
Building muscle mass requires a positive energy balance; therefore, a diet for building muscle must have more calories than you burn.
- To build a pound of muscle mass, you need around 2,800 calories.
- Your body can build around about 227g of muscle each week.
- You may start consuming extra 250 – 500 calories per day, depending on how you gain weight. If it’s easy to gain weight for you – keep to the lower limit; if it’s difficult to gain weight – keep to the end of the range. It takes time to find the right amount of additional calories to build muscle and stay lean.
The critical thing to remember is that your muscle building diet must meet calorie expenditure and provide a healthy and balanced diet that will help you lose fat and get stronger, reaching your bodybuilding dreams.
Macronutrient Ratio
Macronutrient planning is a constituent part of the muscle gain diet plan. Important things to remember:
- 1 – 1.5 grams of protein per pound of your body weight – 25-30 grams of protein (6-8 oz) for a meal. Include proteins like beef, salmon, turkey, chicken, eggs, etc.
- Keep your carbohydrate intake around 150 to 250 grams daily. Go for complex carbs like sweet potatoes, brown rice, oats, beans, and quinoa. They fuel your body, digest slowly, and provide you with energy slowly instead of spikes.
- Simple carbs can be added for post-workout nutrition for quick muscle recovery.
- Fats may vary between 65 to 85 grams a day. Choose avocados, natural butters, coconut oil, extra virgin olive oil, and egg yolks. They are all healthy fats that should be part of your meal plan. Natural fats are used as fuel, while artificial ones just get stored. A healthy diet is always a better choice.
- Add fruit and vegetables, as they are rich in fiber, maintaining intestinal health and functioning.
When bodybuilders want to lose fat without losing their lean muscle, they shift to a higher percentage of protein, up to 35 or 40%.
Bodybuilding Nutrition: Foods to Eat and Avoid
The best diet for muscle gain comes down to healthy nutrition, keeping the right amounts of fats, protein and carbs.
Muscle building foods exclude added sugar, trans fats, and processed food- everything derived from its value, vitamins, and nutrients.
Foods That Form An Effective Muscle-Building Diet
Body building diet plans mainly include the following:
-
Protein Smoothies
As proved by science, protein is an essential macronutrient that helps build muscle, repair tissue after workouts, and make hormones [2]. It’s an essential part of a bodybuilding diet plan.
A protein molecule is made up of chains of smaller compounds – amino acids. The first reason to eat protein is to provide your body with the necessary amino acids to build and repair your muscles.
Regular exercise increases your muscles’ demand for protein intake. Regarding protein powders, some of the highest-quality proteins are whey or casein.
To support muscle growth, eat about 0.8-to-1 gram of protein per pound of body weight per day.
The protein shake is tasty, convenient, and affordable. If you’re trying to gain muscle, mixing protein powder into shakes is an efficient way to boost your daily calorie intake.
As long as a protein shake comes with various flavor options, it will make your menu diverse and filling, helping to fill the gaps in nutrition.
2. Milk
Milk consumption [3] increases muscle protein synthesis and improves muscle protein balance. When post-workout milk consumption is combined with weight training, you may see muscle hypertrophy and lean mass improvements.
Although there’s a belief that full-fat milk has more advantages for our body, low-fat milk has shown the same effect in terms of protein synthesis and post-exercise rehydration, except for those who are lactose intolerant.
3. Brown Rice
Brown rice is considered “whole grain,” unlike its white twin, bringing you more fiber and nutrients. However, regarding calorie intake, the difference between both of them is minor. White rice has a lower glycemic index and higher carb content. Rice after the workout session helps regain strength faster.
4. Protein Bars
A high-quality protein bar will help you improve performance, provide satiety, and add to overall health. The best protein bars are composed of ingredients that fit your dietary needs.
When looking for a protein bar, be sure to read the ingredients. Many brands are well-advertised; however, that’s just effective marketing. Often times the protein bars are full of sugars, fructose, synthetic preservatives, and trans-fat coating instead of chocolate.
Expecting long-term energy, you’ll just feel bloated. When in doubt, go for a peanut butter sandwich, which will work better than these so-called protein bars.
5. Nuts
Nuts are full of protein and healthy fats when consumed fresh and provide you with omega-3 fatty acids. Besides, they are rich in magnesium, which maximizes your muscle power.
Nuts also top off your levels of zinc and iron, which promote muscle strength, called an insulin-like growth factor. Iron is vital for providing myoglobin, a protein that carries and stores oxygen in muscle tissues.
Nuts provide protein for pre-or post-workout nutrition and healthy carbs.
6. Red meat
Meat contains multiple vitamins and minerals essential for muscle gain: zinc, selenium, B vitamins (B 2, B 6, and B 11), and iron in red meat.
Red meat provides quality protein maintaining muscle growth. It also has conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which helps to decrease abdominal fat.
Oily Fish And Salmon
Fish is one of the healthiest foods for bodybuilders and a constituent of a muscle gain diet. In fact, the American Heart Association recommends eating it (fatty varieties, in particular) at least two times a week. Fatty fish is high in two kinds of omega-3 fatty acids – eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which benefit our cardiovascular health.
Salmon provides 38 grams (g) of protein and only 4 g of saturated fat.
7. Potatoes And Starch
Potato protein consumption can increase muscle protein synthesis rates at rest and during recovery from exercise.
A recent study [4] shows that plant-derived proteins can induce strong muscle-building responses.
Researchers at Maastricht University in The Netherlands found that consuming 30 grams of potato-derived protein concentrate after resistance exercise increased muscle protein synthesis rates and didn’t differ from an equivalent amount of milk protein concentrate.
Starch is a type of complex carbohydrate that refills your energy sources.
8. Dry Fruit
Dry fruit is a high in calories snack. Before buying some, ensure there’s no added sugar, which is unnecessary given the natural high fructose levels they initially contain. Consume just dries, not sugar-coated fruits.
Dried fruits contain:
- Antioxidants are crucial for the natural process of detoxification.
- Reducing stress.
- Improving the overall immune system.
9. Healthy Oils
To maintain health and strength, focus on sources of healthy fats from vegetable oils like olive oil, canola oil, and avocados. Nuts and fatty fish such as salmon, herring, sardines, and trout, which are all good sources of protein, also provide healthier types of fat.
10. Avocados
One avocado is an excellent supply of healthy fats – 30 g, and has enough protein – up to 4 g. Moreover, it’s rich in folic acid (B9), which is essential for absorbing protein. Just a perfect combo for a muscle-growing diet.
Foods To Avoid When Building Muscle
It goes without saying that some foods can be detrimental to your health; the laundry list includes processed food, high content of added sugar, trans fats, and alcohol. When consumed in high quantities, they give you nothing but a detrimental effect, though they are typically tasty.
1. Alcohol
Alcohol consumption reduces muscle protein synthesis, which leads to the reduction of a gaining muscle process. It negatively influences hormone levels and decreases the body’s metabolism.
2. Processed Meat
While meat protein is vital for building muscle mass, highly-processed meat is full of chemicals and nitrates. They often have water and sugar to bulk them up and improve flavor, lowering their protein percentage than fresh meats.
Moreover, regular consumption of processed meat increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and cancer, according to the Harvard School of Public Health.
3. Soda And Candy
Eating foods high in added sugar immediately increases your insulin levels, giving energy spikes in the short term. It can be helpful for exercising when your muscles are in a carbohydrate-depleted state, and quick carbs boost your glycogen level and aid muscle recovery. However, go for natural sugars rather than added varieties to avoid their accessive accumulation.
4. Baked Foods
Baked foods are a treasure for a sweet tooth. Generally, they are harmless; however, manufacturers use trans fats to extend the product’s shelf life and lots of refined flour and added sugar.
Trans fats lower your healthy cholesterol levels and raise unhealthy cholesterol ➡ higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Refined flours have the majority of nutrients and fiber removed during processing. Sugar offers no nutrients and can lead to weight gain, diabetes, and heart disease.
Instead, bake at home with the plant oil and wholegrain flour.
5. Salty Snacks
Excess sodium leads to water retention, which causes extra bloating. High-salt foods are typically low in nutrition value and high in fat, which can lead to metabolic disorders.
6. Ice Cream
Ice cream has little nutritional value and lots of added sugar and trans fats. It can only be helpful when we need to consume more calories in a bulking phase.
Bodybuilding Supplements
When planning a diet for gaining muscle, most bodybuilders use supplements to help muscle growth and amplify the effects of their training.
-
Protein
It is an essential supplement since it gives amino acids, which are vital for muscle building when digested. The best protein powders are whey, casein, pea protein, etc. When choosing protein supplements, consider a blend that offers different amino acids.
-
Whey protein
Whey protein powder is easily digestible and quickly sends its amino acids to the muscle tissues. Whey protein contains peptides that increase blood flow to your muscles, enriching them with enough nutrients, oxygen, and hormones when they need it.
-
Casein protein
It is slow to digest, providing a steady flow of amino acids over several hours. Therefore, you can eat it before going to bed when your body is about to stay for several hours without food.
-
Magnesium
Magnesium reduces blood pressure and insulin sensitivity and increases muscle oxygenation when exercising. Magnesium supplements are essential before or after a workout.
-
Creatine
Creatine is an amino acid primarily found in your muscles as well as in the brain. Creatine helps increase anaerobic endurance and power output. To make it easy on your digestive system, it comes in a fine powder form and is easily dissolved. We can also get creatine from seafood and red meat; however, this amount can be far below the required one [5]. Creatine benefits athletes who need short bursts of energy or enhanced muscle strength – such as sprinters, weight lifters, and team sport athletes.
-
BCAAs
The branched chain amino acid is any of the acids included in the group: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. It is critical for stimulating skeletal muscle growth and protein synthesis; that’s why it’s suggested for athletes trying to gain muscle mass and a lean body.
BCAAs are essential amino acids (our body cannot make them); however, a properly planned protein-rich diet can cover your daily needs.
BCAAs are found in:
- meat, poultry, and fish
- eggs
- dairy products, such as milk, greek yogurt, and cheese
- nuts and seeds
- soy products, such as tofu and tempeh
- legumes, including beans, peas, and lentils
-
Beta-Alanine
t is a non-essential amino acid that helps to delay muscle fatigue and boost muscle growth. Beta-alanine improves your workout performance by increasing exercise capacity. It also has antioxidant, immune-enhancing, and anti-aging properties. You can get beta-alanine from carnosine foods (meat, poultry, and fish) or supplements. The recommended dose is 2–5 grams daily.
The Best Diet For Building Muscle: The Effective Meal Plan
Your workout plan is just one part of a deal. Your training regimen must be backed up by a nutrition regimen to produce the best results for your body. While working out, will feel better with easy-digesting carbs and fewer fats before and after workouts to promote energy and muscle growth.
Don’t forget to check the list of best meals for muscle growth :
- Protein: protein powders. egg whites, whole eggs, white meat, white fish, Greek yogurt
- Starches: Brown rice, quinoa, yams, potatoes, oats, and whole-wheat kinds of pasta, bread, cereals, and wraps
- Fruits/vegetables/legumes: Tropical fruits, berries, green/fibrous vegetables, beans
- Oils: Olive oil, coconut oil, nuts/seeds
It’s essential to listen to your body and give it the energy it needs to meet your workout goals and to replenish muscle glycogen.
The Beginner Bodybuilder Meal Plan
Target: 2,500 calories, 218 g carbs, 218 g protein, 83 g fat
This is a plan for newbies who want to stay healthy and start tough workouts. It is a sample for a 150-pound male with a moderately-active lifestyle.
Meal Template
Don’t forget that the best meals for muscle gains integrate fats, proteins and carbs. Don’t go short on them.
Breakfast (700 calories) | 4 whole eggs, scrambled 1 slice cheddar cheese 2 slices whole-wheat toast 1/4 cup sliced avocado |
Snack (330 calories) | 1 scoop whey protein 1/3 cup raw almonds |
Lunch (560 calories) | 5 oz. 95/5 ground beef,
1 tbsp extra-virgin olive oil, 1/2 cup chopped onion,
1 cup shredded lettuce,
2-3 tbsp fresh tomato salsa,
1/4 cup shredded cheddar,
1 tbsp sour cream |
Snack (390 calories) | 2 tbsp all-natural peanut butter,
1 medium apple
1 container 2% Greek yogurt |
Dinner (450 calories) | 6 oz. Atlantic salmon, 1 cup green beans, 2 pat butter |
Breakfast
Boiled Eggs and Protein Oatmeal
That’s quite a traditional beginning of a day for people following a muscle-building diet.
Boiled Eggs – provide you with a very high-quality protein and fat source. The combination with the oatmeal will cover your energy needs for the day ahead.
Oatmeal contains the soluble fiber beta-glucan, which helps digestion and smoothes bowel movements. Besides, oats lower the bad (LDL) cholesterol by 7%, according to studies [6]
Some changes can be added: bananas or dried fruit. Instead of 3 eggs take 2 and a piece of cheese. If you diversify the meals, you’ll never get bored with them.
Basic plate
- 3 boiled eggs
- 1 cup of oatmeal
- 1 scoop of protein powder
Calories: 486
Protein: 35-47g/Fat: 19g/Carbs: 31g/
Lunch
Sweet Potato, Beef, and Roasted Veggie Hash
Roasted vegetables and sweet potatoes are nutritious, easy to make and add vitamins and minerals to your daily diet.
Sweet potato – is high in fiber, and antioxidants, and is rich in beta-carotene, which is converted to vitamin A to support good vision and your immune system.
Vegetables are a valuable source of vitamins, and can suit any taste.
Snacks
Snack | Protein/Fats/Carbs per 100g |
Pumpkin Seeds | 19 g/ 19g /54 g |
Mozzarella Sticks | 15 g/ 19g /25 g |
Peanut Butter | 20 g /50g / 25g |
Almonds | 21.15 g / 50 g / 21.55 g |
Raisins | 3 g / 0.5 g / 79 g |
Figs | 3.3 g / 1g / 64 g |
Dark Chocolate | 5.74 g / 32 g / 58g |
Bananas | 1.10 g / 0.33 g / 22.84 g |
Hazelnuts | 15 g / 62 g / 17g |
Energy balls
(raisins, nuts, honey) | 11 g / 24g / 50 g (approximately) |
Dinner
Ground Beef Fajita Bowl
Fajita bowls are not only tasty but practical. You can change the protein source based on what you prefer: chicken or turkey instead of beef. In case you don’t like rice, try quinoa (an excellent complex carb). If you want more fiber, add black beans.
The basic bowl consists of:
- Meat (2 oz) – stirred until browned.
- Brown rice/quinoa/beans – 2 cups
- Vegetables – stirred and seasoned to taste.
668
What do you need in order to gain pounds of lean muscle and an attractive look?
Physical changes are nothing but advantages and benefits. When you try your hand at bodybuilding, you develop stamina and endurance, enhance your athletic performance, and experience the release of endorphins and mood boosts. Don’t just check your body weight daily – learn to enjoy this challenge and changes.
Evidently, a muscle building diet and sports make the basis for your changes; however, the essential thing is…the appropriate mindset. Doing modifications to your body requires your commitment and non-stop motivation. Any physical alteration, including bodybuilding, starts from the first step in your head. Let this seed of inspiration grow into something bigger – let yourself grow.
FAQs
💪What should I eat for muscle gain❓
💪What do bodybuilders eat for breakfast❓
💪Do Bananas help build muscle❓
💪Which fruit is best for bodybuilding❓
Sources: